

Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-06-23 Origin: Site









When it comes to soldering electronic components, choosing the right tin solder for electronics is crucial for ensuring strong, reliable connections. Among the various solder types available, Sn50 solder stands out due to its balanced composition and excellent performance in electronic applications. This article explores the features, benefits, and applications of Sn50 tin solder for electronics, with a focus on three popular diameters: Sn50 tin solder 0.6mm, Sn50 tin solder 1.0mm, and Sn50 tin solder 1.2mm.
Sn50 tin solder is a leaded alloy composed of 50% tin (Sn) and 50% lead (Pb). This formulation ensures a low melting point, good electrical conductivity, and strong mechanical bonds—making it ideal for solder for electronics. Unlike traditional lead-based solders, Sn50 wire solder is environmentally friendly and complies with modern RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) regulations.
Excellent Conductivity – Ensures minimal resistance in electrical connections.
Low Melting Point – Reduces the risk of damaging sensitive components.
Strong Adhesion – Creates durable solder joints for long-lasting performance.

The diameter of tin wire solder for electronics plays a significant role in soldering precision and efficiency. Below is a detailed comparison of the three most common diameters:
Best for: Fine-pitch PCB components, SMD (Surface Mount Device) soldering.
Advantages:
Ideal for small, delicate joints.
Minimizes excess solder, reducing the risk of bridging.
Perfect for precision electronics like smartphones and microcontrollers.
Best for: General-purpose PCB assembly, through-hole components.
Advantages:
Versatile for both small and medium-sized joints.
Faster soldering compared to 0.6mm wire.
Suitable for DIY electronics and repair work.
Best for: Heavy-duty connections, larger terminals, and power electronics.
Advantages:
Provides more solder per pass, improving efficiency.
Stronger joints for high-current applications.
Great for automotive and industrial electronics.
Sn50 tin solder is widely used in various electronic soldering tasks, including:
PCB Assembly – From consumer gadgets to industrial control boards.
Consumer Electronics Repair – Smartphones, laptops, and gaming consoles.
Automotive Electronics – Wiring harnesses, sensors, and control modules.
LED Manufacturing – Ensuring reliable connections in LED strips and panels.
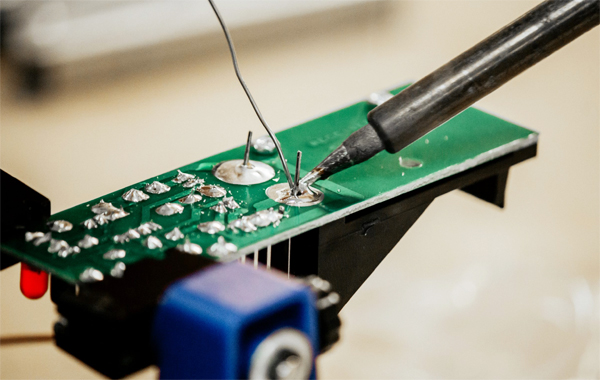
While there are multiple solder alloys available, Sn50 tin solder for electronics offers several advantages:
Better Thermal Fatigue Resistance – Performs well under repeated heating and cooling cycles.
Reduced Oxidation – Flux-cored variants prevent oxidation for cleaner joints.
Cost-Effective – Provides high-quality soldering without the premium price of silver-rich alloys.
To achieve the best results with Sn50 tin solder, follow these soldering best practices:
Use the Right Temperature – Typically between 250°C and 300°C for optimal flow.
Clean Surfaces Before Soldering – Remove oxidation and contaminants for better adhesion.
Choose Flux-Cored Solder – Ensures better wetting and reduces the need for additional flux.
Match the Diameter to the Job – Use 0.6mm for precision, 1.0mm for general use, and 1.2mm for heavy-duty joints.
Whether you're working on intricate PCB repairs or industrial-grade electronics, Sn50 tin solder for electronics provides a reliable and efficient solution. With options like Sn50 tin solder 0.6mm, 1.0mm, and 1.2mm, you can select the perfect diameter for your specific needs. By understanding the properties and applications of Sn50 wire solder, you can ensure high-quality, long-lasting solder joints in all your electronic projects.
For hobbyists, technicians, and manufacturers alike, Sn50 tin solder remains a top choice for its performance, safety, and versatility in modern electronics soldering.
Contact Information:
Email: xfsolder@163.com or xfsolder@gmail.com
WhatsApp/Wechat: +8613450770997